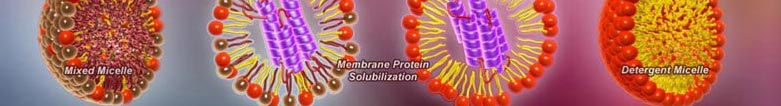
Detergents are amphipathic molecules containing distinct hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces which allow them to act as solubilizing agents. The polar region can form hydrogen bonds with water while the hydrophobic region tends to aggregate into micelles and associate with hydrocarbon and nonpolar domains. The fundamental properties of detergents include: the critical micellar concentration (CMC, the concentration above which micelles form); the Kraft Point (the temperature at which an equilibrium exists between the insoluble crystalline state, the monomeric detergent and the micellar state; this temperature is usually equal to the critical micellar temperature, CMT); the aggregation number (the number of detergent molecules within a micelle, which equals micellar MW/monomeric MW); the Hydrophile-Lipophile Balance (HLB, a measure of the hydrophilic nature of the detergent. An HLB between 12-20 is preferred for non-denaturing solubilization and > 20 for extrinsic protein solubilization); For non-ionic detergents, the Cloud Point is the temperature above the CMT where detergents become cloudy forming a detergent-rich phase and an aqueous layer.
This is useful to separate integral membrane proteins from hydrophilic proteins after first solubilizing at low temperature. Detergents can be grouped into three main classes: Ionic detergents; Non-ionic detergents and Zwitterionic detergents. Ionic detergents have a charged headgroup (anionic or cationic) and are useful for the complete disruption of cells and denaturation of proteins for separation during SDS-PAGE. Some examples include anionic detergents like SDS, cationic detergents such as CTAP and anionic bile salts such as deoxycholate. Non-ionic detergents are useful in the solubilization of membrane proteins since they are able to break lipid-lipid and lipid-protein interactions, but have a limited ability to break protein-protein interactions. They include low CMC detergents such as Triton X-100 and a NP-40 substitute, Tergitol, etc., which cannot be dialyzed away, uncharged bile salts like Big CHAP(which can be dialyzed) and the very dialyzable (CMC ~ 25 mM) alkyl glucosides such as octyl glucopyranoside (OG), dodecyl maltoside, etc. Zwitterionic detergents protect the native state of proteins without changing the native charge of the protein molecules. In addition to solubilization properties alone, zwitterionic detergents are very useful for isoelectric focusing and 2D electrophoresis. Many synthetic zwitterionic detergents are known as sulfobetaines. Sulfobetaines retain their zwitterionic characteristics over a wide range of pH and are widely used for 2D gel electrophoresis.
Non-detergent sulfobetaines (NDSBs) are a group of zwitterionic compounds containing both a cationic and anionic component which do not form micelles because of their small hydrophobic moiety. NDSBs solubilize proteins under mild conditions and can prevent protein denaturation by heat or acid, inhibit protein aggregation, acceleration of protein refolding, and aid membrane protein extraction. They can easily be removed by dialysis.Due to these factors, NDSBs are the preferred agents for denaturant protein purification. NDSBs are able to effectively fold proteins without denaturing the product. Many traditional protein solubilization compounds, such as urea, are not able to accomplish this task without negatively impacting proteomic quality.
Aurora Medbiochem offers a variety of, structurally diverse detergents for protein purification and extraction work. In addition, Aurora Medbiochem offers several non-ionic detergents under “BiopureAct” trade names. These are 10% sterile-filtered detergents treated chemically to remove the aldehydes and peroxides. Aurora Medbiochem also proudly offers manynon-detergent sulfobetaines (NDSBs) for protein purification work.
A zwitterionic detergent useful for the solubilization of proteins including previously undetected membrane proteins. ASB-14 exhibits better protein solubilization properties than CHAPS. Also useful for solubilizing proteins for 2D-gel electrophoresis.
ASB-16 is a useful zwitterionic detergent for the solubilization of proteins including previously undetected membrane proteins. ASB-16 exhibits better protein solubilization properties than CHAPS. Also useful for solubilizing proteins for 2D-gel electrophoresis.
A 10% sterile-filtered solution in water of the zwitterionic detergent CHAPS (Cat. No.# AUR10271).
CHAPS is a zwitterionic a non-denaturing detergent that protects the native state of proteins, able to disrupt non-specific protein interactions and has less protein aggregation than non-ionic detergents. It is electrically neutral and easily removed by dialysis.
Chenodeoxycholic acid is a bile acid that has been shown to increase intracellular Ca2+ in isolated rat hepatocyte couplets. Induces a permeability transition in freshly isolated rat liver mitochondria.
Cholic acid sodium is the sodium salt of the naturally occurring bile acid Cholic acid. Acts as a non-denaturing ionic detergent used for extraction of membrane proteins.
Sodium deoxycholate is a bile salt and an ionic detergent. It has been used in the lysis buffer prepared for brown adipose tissue. It has also been used in the decellularization of aortic valvular conduit.
A highly purified form of deoxycholic acid sodium (Cat. No. AUR10320). Useful as a detergent to solubilize membrane-bound proteins in their native state.
Digitonin, a glycoside obtained from Digitalis purpurea, could increase cell permeability by binding to cholesterol molecules and reduce tumor growth. Digitonin is a natural detergent.
Genapol X-100 has been used in a study to assess how detergents affect inhibitor potencies against cyclo-oxygenase isoforms.
IGEPAL® CA-630 is a nonionic, non-denaturing detergent suitable for solubilization, isolation and purification of membrane protein complexes. It is chemically indistinguishable from Nonidet P-40.
NDSB-195 is a non-detergent sulfobetaine that has been reported to prevent protein aggregation and facilitate the renaturation of chemically and thermally denatured proteins. Zwitterionic over a wide pH range. Easily removed by dialysis